A Comprehensive Guide to Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is a vital component of financial protection for property owners. It safeguards against losses and damages to one’s home and possessions and offers liability coverage for accidents that may occur on the property. This detailed guide explores homeowners insurance, covering its types, benefits, coverage options, and considerations, helping you make an informed decision.

Table of Contents
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024 Navigating the process of filing an insurance c…
Professional Liability Insurance: Best Guide 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions) Professional liab…
Understanding TATA AIG Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Regarding securing the future, nothing stands out quite like insurance. It’s the comforting cushion …
Understanding Ladder Life Insurance 2024: Climbing the Rungs of Financial Security
Ladder Life Insurance: When it comes to securing your financial future and providing for your loved …
Best Guide to Motorcycle Insurance 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Motorcycle Insurance Motorcycle insurance is essential for protecting rider…
Allstate Car Insurance: Comprehensive Coverage and Benefits 2024
Allstate Car Insurance, one of the largest insurance providers in the United States, offers a range …
What is Homeowners Insurance?
Homeowners insurance is a form of property insurance that covers a private residence. It combines various types of insurance protections, including loss of the home, its contents, loss of use (additional living expenses), and liability insurance for accidents that may happen at the home or involve the homeowner.
Key Features of Homeowners Insurance
- Dwelling Coverage: Protects the structure of the home itself, including walls, roof, and built-in appliances.
- Personal Property Coverage: Covers personal belongings within the home, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Protection: Provides coverage if someone is injured on the property or if the homeowner is responsible for damage to someone else’s property.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): Covers the costs of living elsewhere if the home is uninhabitable due to a covered loss.
- Medical Payments Coverage: Pays for medical expenses of guests injured on the homeowner’s property, regardless of fault.
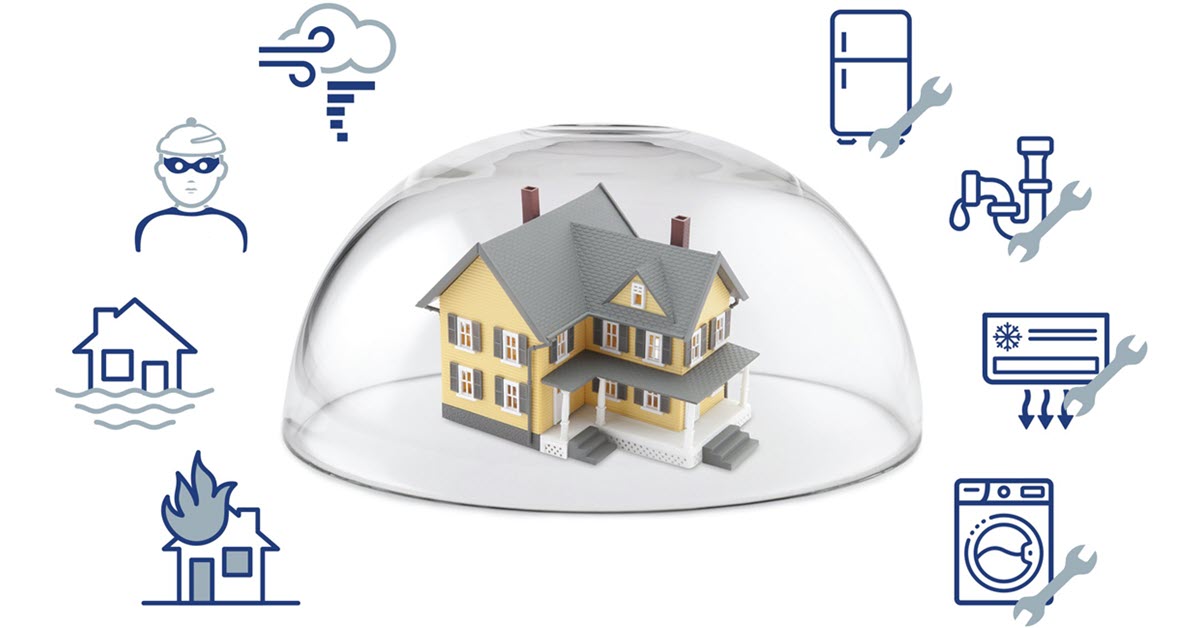

Types of Homeowners Insurance Policies
There are several types of homeowners insurance policies, each designed to meet different needs:
1. HO-1: Basic Form
HO-1 policies offer very limited coverage. They typically cover the home and personal belongings against 10 specific perils: fire, lightning, windstorm, hail, explosion, riots, damage by aircraft, damage by vehicles, smoke, and vandalism.
- Advantages: Lower premiums due to limited coverage.
- Ideal for: Homeowners seeking minimal and specific coverage.
2. HO-2: Broad Form
HO-2 policies provide broader coverage than HO-1, protecting against additional perils such as falling objects, weight of ice/snow/sleet, accidental discharge or overflow of water or steam, sudden tearing apart, cracking, burning, bulging, freezing, and damage from electrical current.
- Advantages: Broader protection compared to HO-1.
- Ideal for: Homeowners wanting more comprehensive coverage than basic forms.
3. HO-3: Special Form
HO-3 is the most common type of homeowners insurance policy. It provides coverage for the home against all perils except those specifically excluded in the policy. Personal belongings are covered against the same perils as HO-2.
- Advantages: Extensive coverage for the dwelling and broad coverage for personal property.
- Ideal for: Most homeowners looking for comprehensive protection.
4. HO-5: Comprehensive Form
HO-5 policies provide the highest level of coverage. They cover both the home and personal belongings against all perils except those specifically excluded.
- Advantages: Broadest coverage available, fewer exclusions.
- Ideal for: Homeowners seeking maximum protection.
5. HO-6: Condo Insurance
HO-6 policies are designed for condominium owners. They cover personal property, interior walls, and fixtures within the condo unit. The condominium association’s policy typically covers the building’s structure and common areas.
- Advantages: Tailored coverage for condo owners.
- Ideal for: Condominium unit owners.
6. HO-8: Older Home Form
HO-8 policies are tailored for older homes where the cost to replace the home exceeds its market value. They offer similar coverage to HO-1 but may cover the home for its actual cash value rather than replacement cost.
- Advantages: Suitable for insuring older homes with unique construction.
- Ideal for: Owners of historic or older homes.
Benefits of Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance offers numerous benefits, providing peace of mind and financial protection:
- Protection Against Property Damage: Covers repair or rebuilding costs due to covered perils such as fire, storms, and vandalism.
- Personal Property Coverage: Reimburses for the loss or damage of personal belongings.
- Liability Coverage: Protects against lawsuits for bodily injury or property damage caused by the homeowner or family members.
- Additional Living Expenses: Covers temporary housing and living expenses if the home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered loss.
- Mortgage Requirement: Most mortgage lenders require homeowners insurance as a condition for granting a loan.
Coverage Options and Riders
Homeowners insurance policies can be customized with additional coverage options and riders to meet specific needs:
- Scheduled Personal Property: Provides additional coverage for valuable items such as jewelry, art, and collectibles.
- Water Backup Coverage: Covers damage from water backup through sewers or drains.
- Flood Insurance: Protects against damage from flooding, which is not covered by standard policies.
- Earthquake Insurance: Covers damage from earthquakes, typically not included in standard policies.
- Identity Theft Protection: Provides assistance and coverage for expenses related to identity theft.
- Home Business Coverage: Offers protection for home-based business equipment and liability.
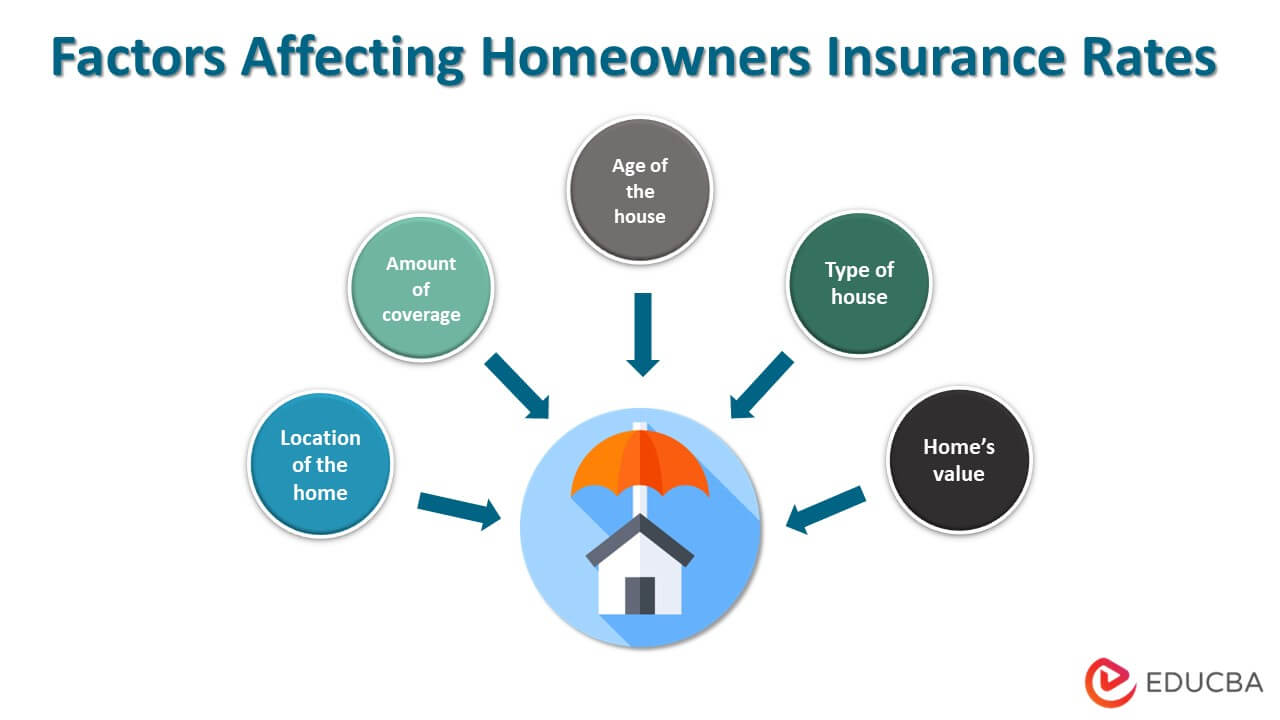
Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Several factors influence the cost of homeowners insurance premiums:
- Location: Homes in areas prone to natural disasters or high crime rates may have higher premiums.
- Home Value and Construction: Higher-value homes or those with unique construction features can result in higher premiums.
- Coverage Amounts: Higher coverage limits and additional coverage options increase premiums.
- Deductible Amount: Choosing a higher deductible can lower premiums but increases out-of-pocket costs in the event of a claim.
- Claims History: A history of frequent claims can result in higher premiums.
- Credit Score: Insurers often use credit scores to determine premiums, with higher scores generally leading to lower rates.

How to Choose the Right Homeowners Insurance Policy
Selecting the right homeowners insurance policy involves careful consideration of several factors:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the level of coverage needed for your home, personal property, and liability.
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare premiums, coverage options, and policy features.
- Evaluate Insurer Reputation: Choose a reputable insurance company with strong financial stability and good customer service.
- Understand Policy Exclusions: Review the policy exclusions to understand what is not covered.
- Consider Additional Coverage: Evaluate whether additional coverage options or riders are necessary to meet your needs.
The Claims Process
Filing a homeowners insurance claim involves several steps:
- Notify the Insurer: Contact the insurance company as soon as possible after a loss or damage occurs.
- Document the Damage: Take photos or videos of the damage and create an inventory of damaged items.
- Complete Claim Forms: Fill out the required claim forms provided by the insurer.
- Provide Documentation: Submit necessary documents, such as repair estimates and proof of ownership.
- Insurer Review: The insurance company reviews the claim and may send an adjuster to assess the damage.
- Approval or Denial: The insurer approves or denies the claim based on the policy terms and documentation provided.
- Receive Payment: If approved, the insurer issues payment for the covered losses.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Homeowners insurance policies often include exclusions and limitations:
- Flood Damage: Standard policies typically do not cover flood damage, requiring separate flood insurance.
- Earthquake Damage: Earthquake damage is generally excluded, requiring separate earthquake insurance.
- Wear and Tear: Damage from normal wear and tear or lack of maintenance is not covered.
- High-Value Items: Standard policies may have coverage limits for high-value items such as jewelry, requiring additional coverage.
- Intentional Damage: Damage caused intentionally by the homeowner or family members is not covered.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Rebuilding After a Fire
The Johnson Family experienced a devastating fire that destroyed their home. Fortunately, they had an HO-3 homeowners insurance policy with sufficient dwelling coverage to rebuild their home and replace their belongings. The additional living expenses coverage allowed them to live in a rental home while their house was being rebuilt, providing financial relief during a challenging time.
Case Study 2: Protecting Valuable Art Collection
Maria, an art collector, purchased an HO-5 policy with a scheduled personal property rider to cover her valuable art collection. When a theft occurred, her policy provided full reimbursement for the stolen pieces, protecting her investment and allowing her to recover financially.
Industry Insights and Statistics
- Prevalence of HO-3 Policies: According to the Insurance Information Institute, HO-3 policies are the most commonly purchased homeowners insurance policies due to their comprehensive coverage.
- Cost of Claims: The average homeowners insurance claim cost has been rising, driven by increases in natural disasters and rebuilding costs.
- Importance of Additional Coverage: Many homeowners opt for additional coverage options, such as flood and earthquake insurance, to protect against risks not covered by standard policies.

Conclusion
Homeowners insurance is a crucial component of financial protection for property owners, offering coverage for the home, personal belongings, and liability. By understanding the key features, benefits, types of policies, and factors affecting premiums, you can make an informed decision about the right homeowners insurance policy for your needs. Whether for protecting against property damage, ensuring liability coverage, or securing additional living expenses, homeowners insurance provides essential peace of mind and financial security.
Sources
- Insurance Information Institute – Homeowners Insurance
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners – Homeowners Insurance
- American Council of Life Insurers – Homeowners Insurance







