A Comprehensive Guide to Earthquake Insurance
Earthquake insurance is a specialized type of property insurance designed to cover damage caused by earthquakes, which are not typically covered by standard homeowners, renters, or business insurance policies. This guide explores the features, benefits, coverage options, and considerations of earthquake insurance to help you understand its importance and how to choose the right policy.

Table of Contents
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024 Navigating the process of filing an insurance c…
Professional Liability Insurance: Best Guide 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions) Professional liab…
Understanding TATA AIG Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Regarding securing the future, nothing stands out quite like insurance. It’s the comforting cushion …
Understanding Ladder Life Insurance 2024: Climbing the Rungs of Financial Security
Ladder Life Insurance: When it comes to securing your financial future and providing for your loved …
Best Guide to Motorcycle Insurance 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Motorcycle Insurance Motorcycle insurance is essential for protecting rider…
Allstate Car Insurance: Comprehensive Coverage and Benefits 2024
Allstate Car Insurance, one of the largest insurance providers in the United States, offers a range …
What is Earthquake Insurance?
Earthquake insurance provides financial protection for property owners in the event of damage caused by seismic activities. Given that earthquakes can cause substantial destruction to buildings and personal property, having a dedicated insurance policy can be crucial for recovery and rebuilding efforts.
Key Features of Earthquake Insurance
- Dwelling Coverage: Protects the physical structure of the home, including the foundation, walls, and roof.
- Personal Property Coverage: Covers personal belongings such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): Pays for temporary housing and related expenses if the home is uninhabitable due to earthquake damage.
- Deductibles: Earthquake insurance policies typically have high deductibles, often expressed as a percentage of the home’s insured value.
- Policy Limits: The maximum amount the insurance company will pay for covered losses.
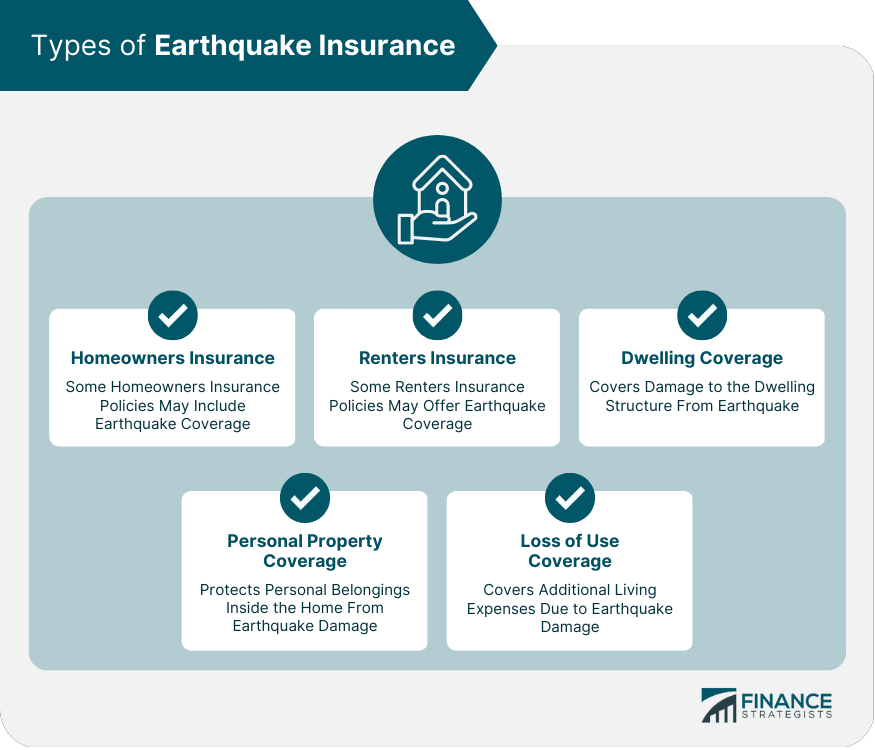
Types of Earthquake Insurance Policies
Earthquake insurance policies can vary based on the type of property and the level of coverage:
- Homeowners Earthquake Insurance: Provides coverage for single-family homes.
- Renters Earthquake Insurance: Covers personal belongings of tenants.
- Condo Earthquake Insurance: Offers coverage for the interior of the unit and personal property, typically excluding the building structure, which is covered by the condo association’s master policy.
- Commercial Earthquake Insurance: Covers non-residential properties, including businesses and commercial buildings.
Benefits of Earthquake Insurance
Earthquake insurance offers several important benefits for property owners:
- Financial Protection: Covers the cost to repair or replace the building and personal belongings damaged by an earthquake.
- Peace of Mind: Provides reassurance that financial losses from earthquakes are covered, reducing stress and uncertainty following a seismic event.
- Compliance with Lender Requirements: Ensures compliance with mortgage lender requirements in earthquake-prone areas.
- Support for Recovery: Helps property owners rebuild and recover more quickly after an earthquake.

Common Perils Covered by Earthquake Insurance
Earthquake insurance typically covers damage directly caused by seismic activity, including:
- Structural Damage: Cracks in walls, foundation damage, and roof collapse.
- Personal Property Damage: Damage to furniture, appliances, electronics, and other personal items.
- Additional Living Expenses: Costs for temporary housing, meals, and other living expenses if the home is uninhabitable.
Factors Affecting Earthquake Insurance Premiums
Several factors influence the cost of earthquake insurance premiums:
- Location: Properties in high-risk earthquake zones, such as California or the Pacific Northwest, typically have higher premiums.
- Building Characteristics: The age, construction materials, and design of the building can impact premiums, with older buildings and those not built to current seismic codes generally costing more to insure.
- Coverage Amounts: Higher coverage limits result in higher premiums.
- Deductible Amount: Choosing a higher deductible can lower premiums but increases out-of-pocket costs in the event of a claim.
- Foundation Type: Buildings with a raised foundation may have higher premiums compared to those on a slab foundation.
How to Choose the Right Earthquake Insurance Policy
Selecting the right earthquake insurance policy involves careful consideration of several factors:
- Assess Your Earthquake Risk: Determine the earthquake risk for your property using seismic maps and other resources.
- Understand Coverage Needs: Evaluate the level of coverage needed for the building and personal belongings.
- Compare Policies: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare premiums, coverage options, and policy features.
- Review Policy Exclusions: Understand what is not covered by the policy, such as damage from landslides or tsunamis triggered by an earthquake.
- Consider Additional Coverage: Evaluate whether additional endorsements or riders are necessary to meet your needs, such as coverage for masonry veneer or swimming pools.
The Claims Process
Filing an earthquake insurance claim involves several steps:
- Notify the Insurer: Contact the insurance company as soon as possible after an earthquake.
- Document the Damage: Take photos or videos of the damage and create an inventory of damaged property.
- Complete Claim Forms: Fill out the required claim forms provided by the insurer.
- Provide Documentation: Submit necessary documents, such as repair estimates and proof of ownership.
- Insurer Review: The insurance company reviews the claim and may request additional information or send an adjuster to assess the damage.
- Approval or Denial: The insurer approves or denies the claim based on the policy terms and documentation provided.
- Receive Payment: If approved, the insurer issues payment for the covered losses.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Earthquake insurance policies often include exclusions and limitations:
- Earth Movement Other Than Earthquake: Damage from landslides, sinkholes, and subsidence is typically not covered.
- Flood Damage: Flooding resulting from an earthquake, such as a tsunami, is not covered by standard earthquake insurance policies; separate flood insurance is required.
- Fire Damage: Fire damage caused by an earthquake is usually covered under a standard homeowners policy, not earthquake insurance.
- Masonry Veneer: Damage to masonry veneer, such as brick or stone facing, may be excluded or limited.
- Vehicles: Damage to vehicles is not covered; a separate auto insurance policy with comprehensive coverage is needed.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Earthquake Damage to a Residential Property
John, a homeowner in California, experienced significant structural damage to his home due to a major earthquake. His earthquake insurance policy provided coverage for the repairs to the foundation, walls, and roof, as well as replacement of damaged personal property. The financial assistance from his earthquake insurance policy allowed him to rebuild and recover without incurring substantial debt.
Case Study 2: Commercial Earthquake Insurance for a Business
Lisa, a small business owner, faced extensive damage to her commercial property after an earthquake. Her commercial earthquake insurance policy covered the cost of repairing the building and replacing damaged inventory and equipment. Without this coverage, Lisa would have struggled to reopen her business and continue operations.
Industry Insights and Statistics
- Seismic Risk Areas: According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), states like California, Alaska, and Washington have the highest seismic risk, making earthquake insurance especially important for residents in these areas.
- Average Cost: The average cost of earthquake insurance varies widely based on location, building characteristics, and coverage amounts. Premiums can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars annually.
- Underinsurance: Despite the risks, many property owners in earthquake-prone areas remain uninsured or underinsured, exposing them to significant financial loss in the event of an earthquake.
Conclusion
Earthquake insurance is a crucial safeguard for property owners in earthquake-prone areas, providing protection for the building, personal belongings, and financial security in the event of a seismic event. By understanding the key features, benefits, types of policies, and factors affecting premiums, you can make an informed decision about the right earthquake insurance policy for your needs. Whether for protecting against structural damage, ensuring compliance with lender requirements, or securing peace of mind, earthquake insurance offers valuable protection against one of nature’s most destructive forces.
Sources
- Insurance Information Institute – Earthquake Insurance
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) – Earthquake Insurance
- United States Geological Survey (USGS) – Earthquake Hazards Program


















