Comprehensive Guide to Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides lifelong coverage and includes a cash value component. Unlike term life insurance, which covers you for a specific period, whole life insurance remains in force as long as you continue to pay the premiums. This guide delves into the details of whole life insurance, including its features, benefits, drawbacks, and considerations to help you make an informed decision. Vision Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
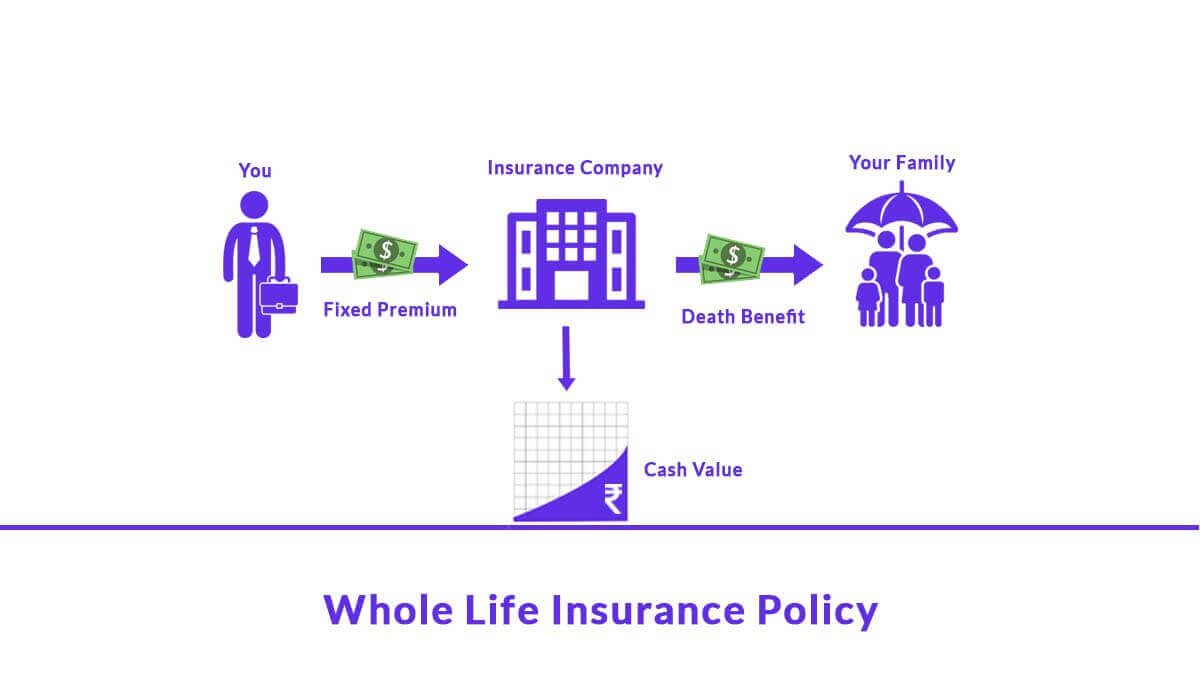
Table of Contents
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Sun Life Insurance Claim: A Comprehensive Guide 2024 Navigating the process of filing an insurance c…
Professional Liability Insurance: Best Guide 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions) Professional liab…
Understanding TATA AIG Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide 2024
Regarding securing the future, nothing stands out quite like insurance. It’s the comforting cushion …
Understanding Ladder Life Insurance 2024: Climbing the Rungs of Financial Security
Ladder Life Insurance: When it comes to securing your financial future and providing for your loved …
Best Guide to Motorcycle Insurance 2024
A Comprehensive Guide to Motorcycle Insurance Motorcycle insurance is essential for protecting rider…
Allstate Car Insurance: Comprehensive Coverage and Benefits 2024
Allstate Car Insurance, one of the largest insurance providers in the United States, offers a range …

What is Whole Life Insurance?
Whole life insurance provides coverage for the insured’s entire lifetime, as long as premiums are paid. In addition to the death benefit, it includes a cash value component that grows over time. This cash value can be accessed through loans or withdrawals, providing a financial resource during the policyholder’s lifetime.
Key Features of Whole Life Insurance
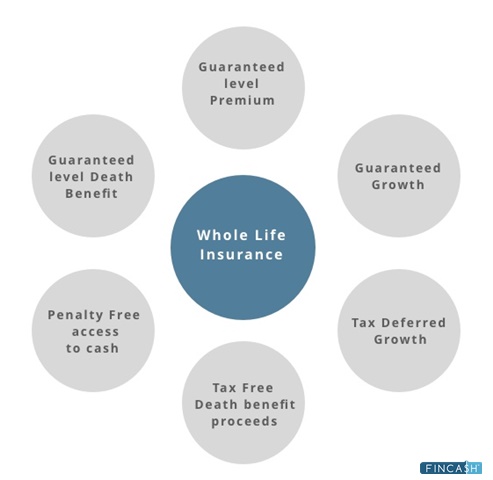
- Lifelong Coverage: Whole life insurance remains in effect for the policyholder’s entire life, provided premiums are paid.
- Fixed Premiums: Premiums are typically fixed and do not increase over time.
- Cash Value Accumulation: Part of the premium payments goes into a cash value account that grows over time, tax-deferred.
- Guaranteed Death Benefit: The death benefit is guaranteed and will be paid out to beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death.
- Dividends: Some whole life policies pay dividends, which can be used to reduce premiums, purchase additional coverage, or accumulate interest.
Types of Whole Life Insurance
There are several types of whole life insurance policies, each with its own features and benefits:
1. Traditional Whole Life Insurance
Traditional whole life insurance is the most straightforward type of whole life policy. It offers a fixed premium, guaranteed death benefit, and guaranteed cash value growth.
- Advantages: Predictable premiums and benefits, guaranteed cash value growth.
- Ideal for: Individuals seeking stable, lifelong coverage with guaranteed benefits.
2. Participating Whole Life Insurance
Participating whole life insurance pays dividends to policyholders. These dividends are a portion of the insurer’s profits and can be used in various ways, such as reducing premiums or purchasing additional coverage.
- Advantages: Potential for dividends, which can enhance the policy’s value.
- Ideal for: Policyholders looking for a potential return on their premiums through dividends.
3. Limited Payment Whole Life Insurance
Limited payment whole life insurance allows policyholders to pay premiums for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. After the payment period, the policy is considered paid up, and coverage continues for life without additional premiums.
- Advantages: Shorter premium payment period, lifelong coverage after premiums are paid.
- Ideal for: Individuals who prefer to pay off their insurance policy in a set number of years.
4. Single Premium Whole Life Insurance
Single premium whole life insurance involves a one-time, lump-sum premium payment. The policy is fully paid up from the beginning, and coverage lasts for the policyholder’s lifetime.
- Advantages: One-time payment, immediate cash value accumulation, lifelong coverage.
- Ideal for: Individuals with a large sum of money to invest in a life insurance policy upfront.
Benefits of Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance offers numerous benefits, making it a valuable financial tool for many individuals and families:
- Lifelong Coverage: Provides peace of mind with lifelong protection for your loved ones.
- Cash Value Growth: Accumulates cash value over time, which can be accessed through loans or withdrawals.
- Fixed Premiums: Predictable premium payments make budgeting easier.
- Dividends: Participating policies can pay dividends, enhancing the policy’s value.
- Tax Advantages: Cash value grows tax-deferred, and death benefits are generally tax-free for beneficiaries.
- Estate Planning: Provides liquidity to cover estate taxes and other expenses, helping preserve the estate’s value.
Drawbacks of Whole Life Insurance
Despite its advantages, whole life insurance also has some drawbacks:
- Higher Premiums: Whole life insurance premiums are significantly higher than term life insurance premiums.
- Complexity: Whole life policies can be more complex to understand compared to term life insurance.
- Slow Cash Value Growth: Cash value accumulation can be slow in the early years of the policy.
- Surrender Charges: Cancelling the policy early may result in surrender charges, reducing the cash value received.
Factors Affecting Whole Life Insurance Premiums
Several factors influence the cost of whole life insurance premiums:
- Age: Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums, as they are considered lower risk.
- Health: Medical history and current health status play significant roles in determining premiums. Healthier individuals usually pay lower premiums.
- Gender: Women often pay lower premiums than men due to longer life expectancies.
- Coverage Amount: Higher death benefit amounts lead to higher premiums.
- Policy Type: Different types of whole life policies (e.g., traditional, participating, limited payment) have different premium structures.
- Lifestyle: Risky behaviors, such as smoking or participating in hazardous activities, can increase premiums.
- Riders: Adding riders or additional benefits to the policy can increase premiums.
How to Choose the Right Whole Life Insurance Policy
Selecting the right whole life insurance policy involves careful consideration of several factors:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your financial goals, coverage needs, and budget to choose the appropriate policy.
- Compare Policies: Obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare premiums, policy features, and benefits.
- Understand Cash Value: Evaluate the cash value growth and how it fits into your overall financial plan.
- Review Dividends: If considering a participating policy, understand how dividends work and how they can benefit you.
- Check Insurer Reputation: Choose a reputable insurance company with strong financial stability and good customer service.
- Consider Riders: Explore optional riders, such as accelerated death benefits or long-term care riders, to enhance your policy.
The Claims Process
Filing a claim for whole life insurance involves several steps:
- Notify the Insurer: Contact the insurance company as soon as possible after the policyholder’s death.
- Complete Claim Forms: Fill out the required claim forms provided by the insurer.
- Provide Documentation: Submit necessary documents, such as the death certificate and proof of identity.
- Insurer Review: The insurance company reviews the claim and may request additional information.
- Approval or Denial: The insurer approves or denies the claim based on the policy terms and documentation provided.
- Receive Benefit: If approved, the death benefit is paid to the beneficiaries, usually as a lump sum.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Whole life insurance policies often include exclusions and limitations:
- Suicide Clause: Policies typically exclude coverage for suicides within the first two years of the policy.
- Misrepresentation: Providing false or misleading information on the application can result in claim denial.
- High-Risk Activities: Deaths resulting from high-risk activities, such as skydiving or scuba diving, may be excluded.
- War and Terrorism: Some policies exclude deaths resulting from acts of war or terrorism.

Case Studies
Case Study 1: Estate Planning and Legacy
Robert, a successful businessman, purchased a participating whole life insurance policy with a $2,000,000 death benefit. He chose this policy to ensure his family would have the necessary funds to cover estate taxes and preserve his estate’s value. The dividends from the policy also allowed Robert to purchase additional coverage over time, further enhancing his legacy for his heirs.
Case Study 2: Financial Security for Dependents
Lisa, a single mother with two young children, opted for a traditional whole life insurance policy with a $500,000 death benefit. This policy provided her with peace of mind, knowing that her children would be financially protected and have the necessary funds for living expenses and education if she passed away.
Industry Insights and Statistics
- Popularity of Whole Life Insurance: According to the Insurance Information Institute, whole life insurance policies account for about 33% of all life insurance policies in force in the United States.
- Cash Value Growth: The cash value component of whole life insurance can serve as an important financial resource, with policyholders often using it for retirement planning, emergencies, or large purchases.
- Policy Loans: Policyholders frequently use whole life insurance loans as a source of tax-advantaged borrowing, with the ability to access the cash value without incurring taxes.

Conclusion
Whole life insurance is a valuable financial tool that provides lifelong coverage, guaranteed death benefits, and cash value accumulation. It offers numerous benefits, including fixed premiums, potential dividends, and tax advantages, making it an attractive option for individuals seeking permanent life insurance. By understanding the key features, benefits, drawbacks, and factors affecting premiums, you can make an informed decision about whether whole life insurance is the right choice for you. Whether for estate planning, financial security for dependents, or building cash value, whole life insurance offers valuable protection and peace of mind.
Sources
- Insurance Information Institute
- American Council of Life Insurers
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners







